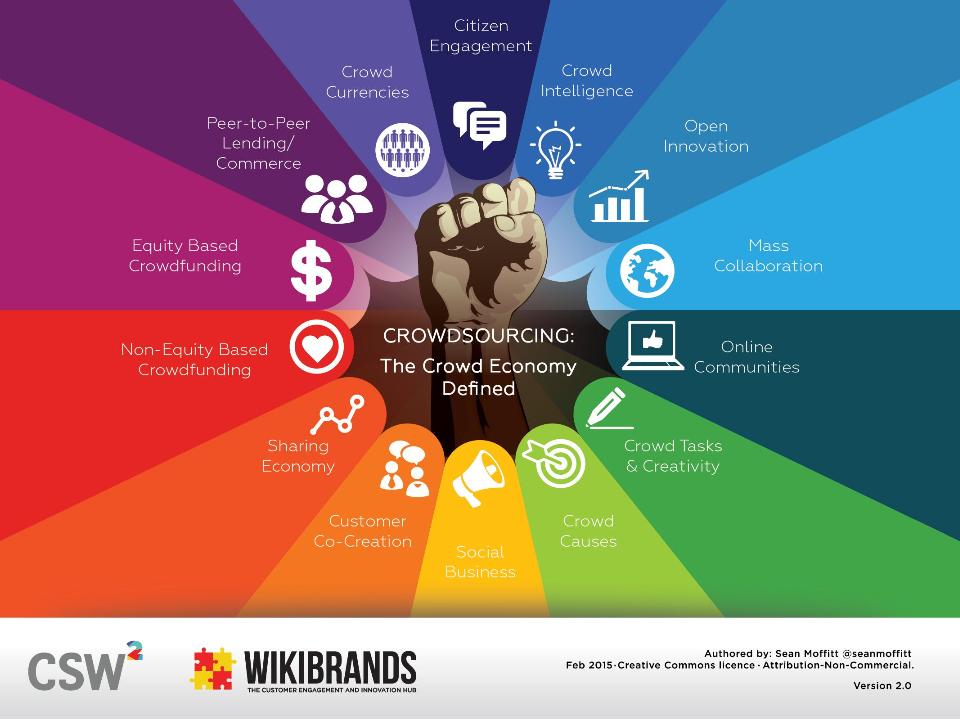
14 Parts of the Crowd Economy
Think about all that time humans spend on social networks or video sharing sites. How much of that effort has an organizational or societal value to it? Is there another way of interacting online that can be more socially productive?
Compared to previous big web movements, the Crowd Economy is considered faster, fairer, cheaper and better than alternatives. To fully understand the crowdsourcing landscape, check out our guide to the 14 Parts of the Crowd Economy.
This guide divides and defines the main 14 ways crowdsourcing is driving business and societal value, from the most directly monetary-focused to the most directly society-community driven (although there is natural connectivity between even the polar ends of the crowd landscape).
#1 Crowd Currencies
Alternative currencies moderated and balanced by the crowd in a distributed, decentralized and publicly-known manner. You may have heard them referred to as digital currencies or cryptocurrencies.
#2 Peer-to-Peer Lending / Commerce
Direct social lending and socialized commerce between people without a financial or retail intermediary.
#3 Equity-Based Crowdfunding
Members of the crowd become part-owners of a company which is raising funds in the form of offering shares and dividends.
#4 Non-Equity Based Crowdfunding
Members of the crowd give money to support a worthy cause or as an exchange for a “reward,” typically the product or service that the crowdfunding company produces or provides.
#5 Sharing Economy
A collaborative economic model built around the sharing of human and physical resources including shared creation, production, distribution, trade and consumption of goods, space, travel and services by different people and organizations.
#6 Co-Creation
A partnership between an organization and a crowd (often customers) to jointly produce a mutually valued outcome while encouraging a more active involvement from the crowd to create a value rich experience.
#7 Social Business
Companies who encourage genuine listening, sharing, engagement and commerce through open, social channels to create value across the corporation or within various functions.
#8 Crowd Causes
Individuals, not-for-profits or purpose-driven organizations, who engage collectively with passionate and interested stakeholders to raise the profile, impact and fundraising potential of their causes.
#9 Crowd Tasks and Creativity
The effort of obtaining requested labor, services, solutions, ideas, or content by soliciting contributions from groups of people, typically online and geographically dispersed, rather than via traditional employees or suppliers.
#10 Online Communities
Groups of individuals gathering and participating on web-based platform(s) and interacting with one another on an ongoing basis driven by a common, tribal attraction for a belief, idea, product, brand, idea, cause or business.
#11 Mass Collaboration
A form of collective action that occurs when large numbers of people work independently on a single project, often modular in nature, that produce shared understandings and outputs.
#12 Open Innovation
Use of inflows and outflows of knowledge to accelerate innovation inside organizations, and expand markets for external applications, through more permeable, open organizational boundaries and combining the organization’s resources with external co-operators.
#13 Crowd Intelligence
The shared or group intelligence and insight that emerges from the collaboration, collective efforts, and/or competition of many individuals.
#14 Civic Engagement
Digitally-connected platforms and activities to help inform, organize, empower and mobilize citizens, communities, national, regional and global movements.
Where does your business figure in this classification? Does this breakdown help you define your organization scope and mission within the crowd economy?
Our consultancy group Hyperloop Innovation can help your organization utilize crowdsourcing to drive business and societal value, through not just ancillary benefits, but by incorporating its principles into your organizational DNA. Check out how you can work together with us to learn more about what makes up the Crowd Economy.
